AI in Cybersecurity: How Xfenser Enables Offensive and Defensive Intelligence in the Era of Autonomous Agents
In recent years, we have witnessed a structural shift in cybersecurity. Artificial intelligence is no longer merely a task accelerator; it is becoming a core element for addressing offensive and defensive challenges in a scalable, timely, and context-aware manner. This trend is not theoretical: in 2025, Anthropic published a report documenting what it describes as the first AI-orchestrated cyber espionage campaign, in which a generative model was manipulated to conduct a sophisticated attack against dozens of organizations with an unprecedented level of autonomy.
This case represents a concrete turning point in how threats and defenses must coexist in the age of AI—and it explains why Xfenser places its technology at the center of both automated penetration testing and active defense within SOCs (Security Operations Centers) and threat analysis processes.
Xfenser: an AI-augmented platform for offensive & defensive security
Xfenser is a platform born from the BackBox.org community, a long-standing presence in the cybersecurity landscape that has developed open-source tools for penetration testing and offensive analysis. This community-driven origin provides a competitive advantage: technologies and methodologies developed from the ground up by professionals and experts, with a practical and concrete focus on real market needs.
The result is an AI-assisted cybersecurity platform that integrates offensive and defensive capabilities within a single framework.
1. Offensive Security — AI-Assisted Pentesting
Xfenser’s penetration testing component leverages highly specialized AI profiles that:
- decompose complex activities into intelligent sub-tasks;
- orchestrate sequences of reconnaissance, enumeration, exploit discovery, and chaining;
- collaborate with traditional tools and AI models to automate analysis and code generation;
- maintain persistent context and operational traceability.
This architecture overcomes the limitations of many “script-based” solutions, as it enables true adaptive reasoning across the attack lifecycle, while remaining under human supervision.
2. Defensive Security — SOC Automation and Threat Analysis
Xfenser’s value is not limited to offensive capabilities: the same technology can be used to strengthen defenses:
- Automated Security Operations Centers (SOCs): Xfenser can analyze event logs, correlate attack signals, and trigger AI-driven automated response workflows.
- Threat hunting and triage: the platform supports defensive teams in identifying indicators of compromise and anomalous behavioral patterns more effectively than traditional approaches.
- Proactive attack simulation: the ability to generate realistic attack campaigns allows organizations to test their defenses under near-real conditions, improving resilience and response times.
This hybrid positioning—offensive and defensive—distinguishes Xfenser from many technologies that focus on only one side of the equation.
The Anthropic report: a warning signal and a confirmation
According to Anthropic’s November 2025 report, a cyber-espionage group exploited agent-like AI capabilities to automate an entire attack chain: from reconnaissance to privilege escalation, through credential harvesting, data analysis, and exfiltration. In that case, AI autonomously executed between 80% and 90% of tactical operations, requiring human intervention only at the most critical decision points (Anthropic).
This dynamic highlights two fundamental aspects:
- The dual nature of AI in cybersecurity: the same technology can amplify both attacks and defenses, depending on who uses it and how.
- The importance of an assisted approach to defense: the speed and scale of AI-based attacks require defensive teams to integrate AI systems for threat detection, incident response, and security orchestration.
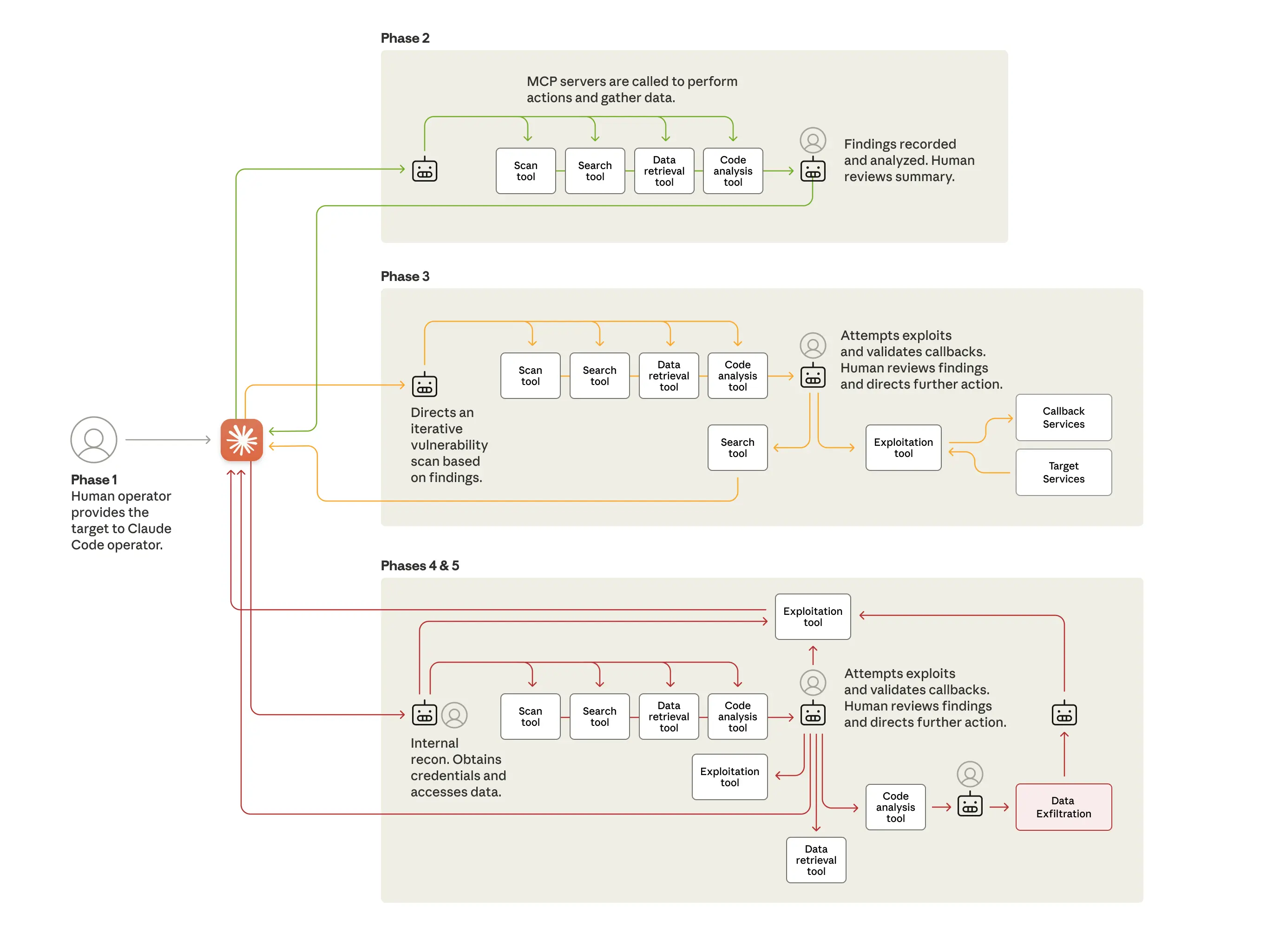
Overcoming AI limitations in pentesting and defense
Despite its growing effectiveness, AI integration into cybersecurity processes still presents technical and operational limitations.
🔹 Dependence on general-purpose models
Third-party AI models are often subject to constraints and limitations: safety filters, limited context windows, and potential hallucinations in outputs. These characteristics make direct use for exploits and advanced tactics difficult without appropriate mitigations.
🔹 Prompt engineering and contextualization
To ensure reliable results, careful prompt engineering is essential. Providing clear context, maintaining operational memory, and ensuring that models “understand” technical security constraints requires experience and structured methodologies.
🔹 Human supervision and validation
Full automation remains a goal rather than a reality. Activities such as interpreting complex risks, adapting strategies in real time, or deciding on mitigations still require human expertise. Human governance remains essential to avoid errors and operational risks.
An AI ecosystem for modern cybersecurity
Xfenser addresses these limitations with a pragmatic approach:
- Dynamic model selection based on the specific task
- Multi-level validation pipelines to verify the reliability of generated results
- Governance controls that include human checkpoints for critical actions
This approach maintains a balance between operational autonomy and security, reducing the risk of errors and building trust in AI-driven operations.
Conclusion — Toward a future of intelligent defense and attack
Xfenser has demonstrated effective capabilities in both offensive (pentesting) and defensive (SOC automation, threat analysis) domains, combining AI, operational intelligence, and human governance. Results from real-world use cases, technical competitions, and benchmarks show how AI technology can act as a capability multiplier in cybersecurity, but not as a replacement for human expertise.
The platform is continuously evolving to increase autonomy, reliability, and analytical depth, while maintaining a strong focus on responsibility and security. To accelerate this path, we are evaluating strategic partnerships and funding opportunities, with the goal of consolidating an AI security ecosystem that is equally effective in defense and proactive vulnerability assessment.
In a world where threats move at algorithmic speed, defense must evolve just as rapidly—and Xfenser is designed to lead that evolution.